How to Check for Low Memory on a Computer
Signs of low memory in a computer include slow performance, frequent crashes or freezes, error messages, and high disk usage. These issues may indicate that the computer needs an upgrade to address a lack of available physical memory.
Framework IT best practices recommend a device with at least 8 GB RAM.
To check for low memory (RAM) on a computer, you can use the following methods:
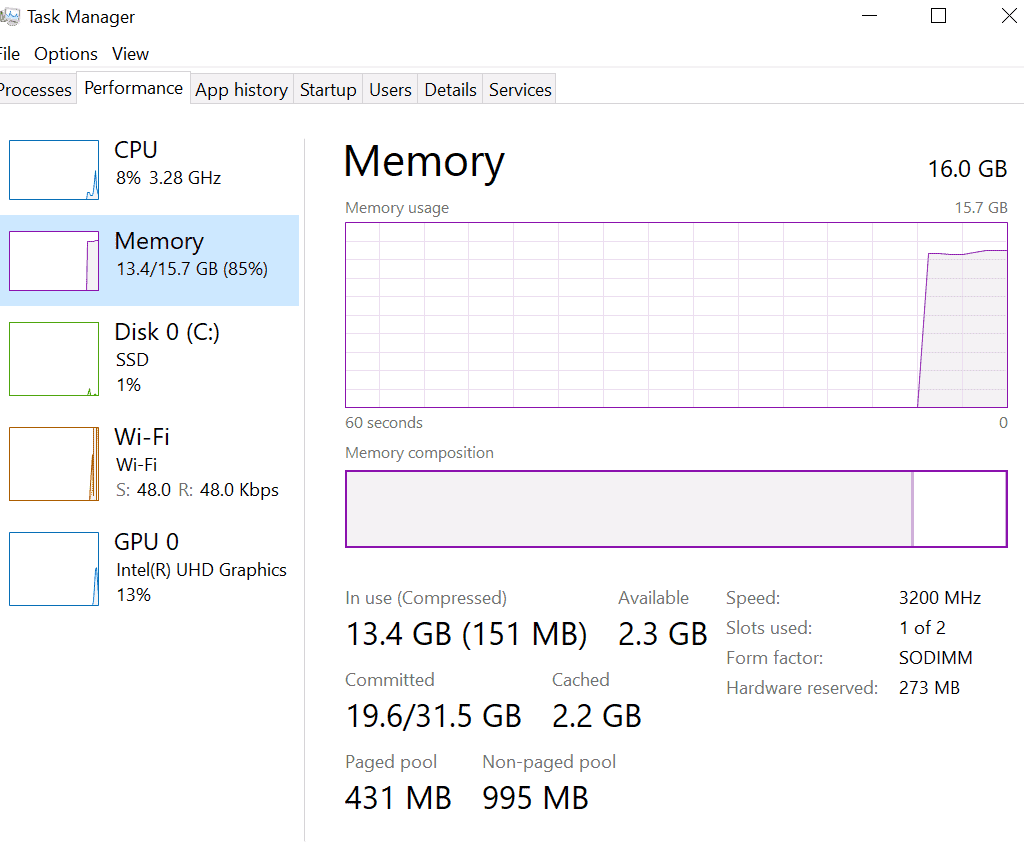
- Using the Task Manager: Open the Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc) and go to the “Performance” tab. The memory usage displays as a graph; if the computer runs low on memory, the chart will be primarily red.
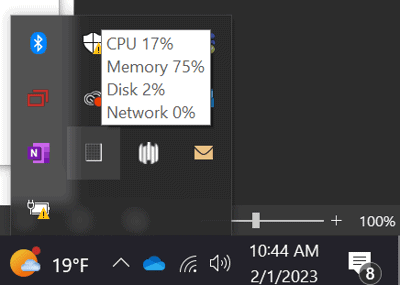
- Using the System Tray: Look for memory usage in the system tray (bottom right corner of the screen). A computer with low memory will have a small icon indicating the amount of used and available memory.
- Using the Command Prompt: Open the Command Prompt (Start menu > type “cmd” and select it) and type “wmic memorychip get capacity” and press Enter. This process will show the total amount of installed memory and the amount of free memory.
- Using a third-party tool: Third-party tools can provide more detailed information about memory usage and help you identify which programs and processes use the most memory. Some examples include Process Explorer, Task Manager Deluxe, and Memory Monitor. Framework IT’s remote monitoring and management software can provide all this information.
It’s vital to regularly check for low memory because it can cause performance issues, such as slow performance, freezing, and crashing of programs. If the computer is low on memory, consider closing unnecessary programs, disabling startup programs, or upgrading the memory.
Check out our blog for ways to boost productivity and streamline workflow. Whether you’re looking for ways to stay organized, improve your time management, or make better use of your technology, we have something for you.

